Weight Gain in Pregnancy: A Trimester by Trimester Guide Backed by Science
Gaining weight during pregnancy is natural and essential for supporting your baby’s development. However, the amount of weight gain matters. Gaining too little or too much can increase risks for both mother and baby. This article provides a trimester-by-trimester breakdown of healthy weight gain, based on guidelines from the Institute of Medicine (IOM), and explains why it matters for your health and your baby’s growth.
Why Weight Gain Matters in Pregnancy
Appropriate weight gain helps ensure:
- Your baby receives adequate nutrients
- Lower risk of complications such as preterm birth or gestational diabetes
- Healthier postpartum recovery
- Lower chance of childhood obesity in your baby
How Much Should You Gain Overall?
The total recommended weight gain during pregnancy depends on your pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI). According to the IOM guidelines:
| Pre-Pregnancy BMI | Weight Status | Recommended Weight Gain |
|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | Underweight | 28–40 lbs (12.5–18 kg) |
| 18.5–24.9 | Normal weight | 25–35 lbs (11.5–16 kg) |
| 25–29.9 | Overweight | 15–25 lbs (7–11.5 kg) |
| ≥30 | Obese | 11–20 lbs (5–9 kg) |
Note: These ranges apply to women pregnant with a single baby. For twins, recommendations are higher.
First Trimester (Weeks 1–13)
Expected weight gain: 1–4.5 lbs (0.5–2 kg)
During the first trimester, your baby is still very small, so the weight gain is minimal. Much of this weight may come from increased blood volume and the development of the placenta.
Tips:
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods even if appetite is low due to nausea
- Don’t stress if weight gain is slow or fluctuating early on
- Stay hydrated and aim for small, frequent meals
Second Trimester (Weeks 14–27)
Expected weight gain: About 1 lb (0.45 kg) per week
This is typically the period of most steady weight gain. Your baby is growing rapidly, your uterus is expanding, and your body is storing fat to prepare for breastfeeding.
Tips:
- Choose high-quality proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Exercise moderately (unless advised otherwise) to manage healthy gain
- Monitor for excessive gain—rapid increase could indicate fluid retention or gestational issues
Third Trimester (Weeks 28–40)
Expected weight gain: About 0.5–1 lb (0.2–0.45 kg) per week
Weight gain continues but may slow in the last few weeks. The baby is gaining fat and finishing organ development. Some of your gain may now come from increased amniotic fluid and breast tissue.
Tips:
- Watch portion sizes—your metabolism may slow slightly as labor nears
- Maintain light activity (like walking or stretching) to support circulation and digestion
- Keep your care provider updated if there are any concerns with weight trends
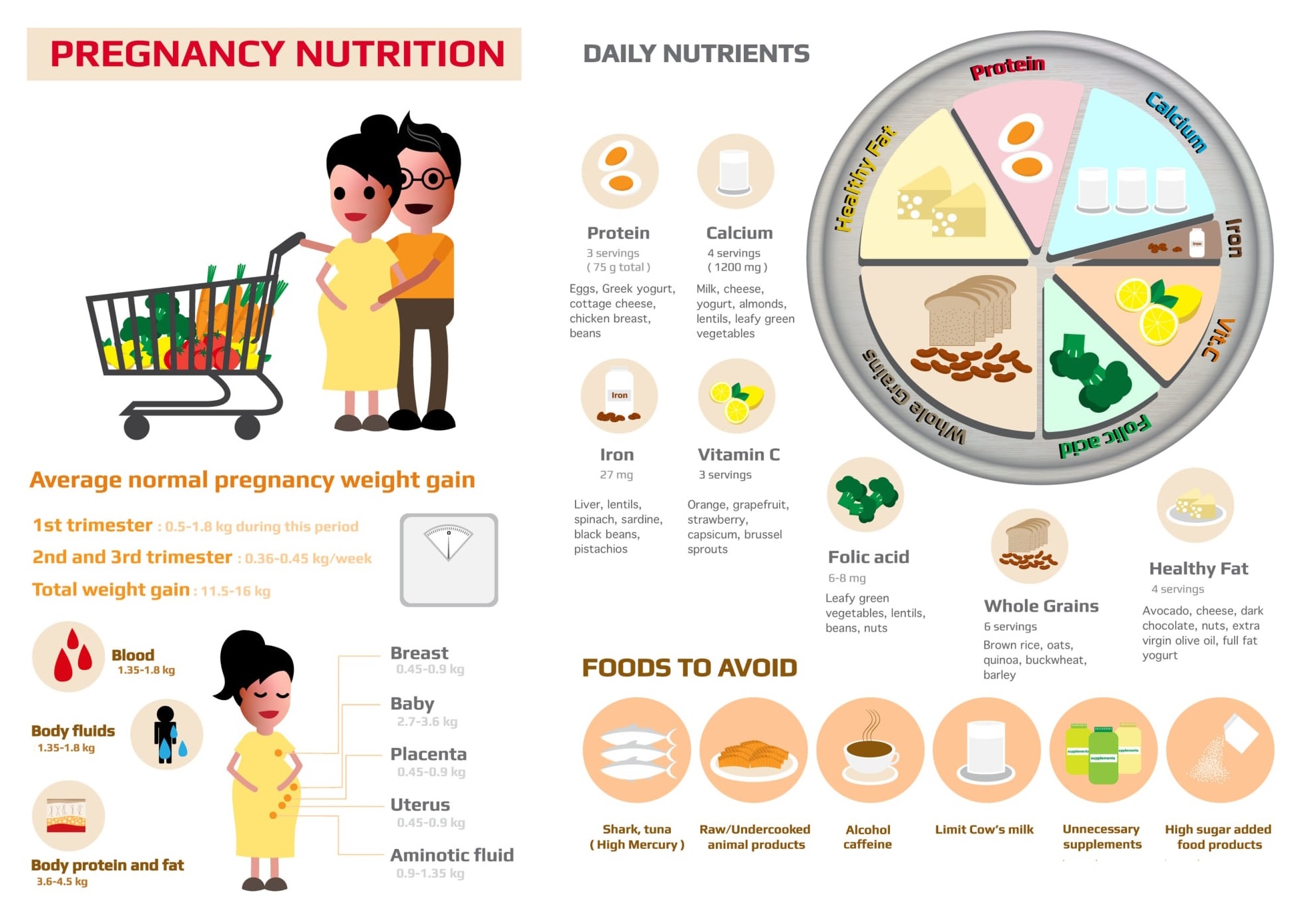
Where Does the Weight Go?
A healthy weight gain doesn’t just go to the baby. Here's a breakdown of where the weight typically goes by delivery:
- Baby: ~7.5 lbs (3.4 kg)
- Placenta: ~1.5 lbs (0.7 kg)
- Amniotic fluid: ~2 lbs (0.9 kg)
- Breast tissue: ~2 lbs (0.9 kg)
- Blood supply: ~4 lbs (1.8 kg)
- Stored fat: ~7 lbs (3.2 kg)
- Uterus growth: ~2 lbs (0.9 kg)
What If You Gain Too Much or Too Little?
Too much weight gain may lead to:
- Increased risk of cesarean delivery
- Gestational diabetes or hypertension
- Higher birth weight (macrosomia)
- Postpartum weight retention
Too little weight gain may lead to:
- Preterm birth
- Low birth weight
- Delayed fetal growth
Monitoring your weight gain with your healthcare provider can help catch any concerns early.
Healthy Habits for Managing Pregnancy Weight Gain
- Eat whole, unprocessed foods most of the time
- Follow prenatal vitamin recommendations
- Exercise regularly with guidance from your doctor
- Listen to your hunger cues
- Stay consistent with prenatal checkups
Conclusion
Weight gain is a normal and necessary part of pregnancy, but it’s important to aim for healthy, science-backed targets. The IOM guidelines offer a helpful framework, but each pregnancy is unique. Use this trimester-by-trimester guide as a starting point—and work closely with your healthcare provider to support a healthy journey for both you and your baby.
FAQs
- What if I gain weight too quickly?
- Check in with your doctor. Sudden weight gain may signal fluid retention or gestational complications.
- Do I need to eat for two?
- Not quite. Most women only need about 300 extra calories per day in the second and third trimesters.
- Can I lose weight during pregnancy?
- Intentional weight loss is not recommended. However, some women with high pre-pregnancy BMIs may gain less weight or maintain their weight with medical supervision.
- How often should I check my weight?
- At every prenatal appointment, and optionally at home between visits if your provider recommends it.
- What’s the best way to eat healthy during pregnancy?
- Focus on variety, balance, and whole foods. Limit processed snacks and sugary drinks.
It takes a village to raise a child !
Join our Facebook group Preschools & Kindergartens in Hong Kong to interact with other parents.